E1 reaction elimination unimolecular E1 reaction mechanism and e1 practice problems Elimination reaction : e1 and e2 reaction – examples, mechanism
E1 vs E2: Comparing the E1 and E2 Reactions - Master Organic Chemistry
Coordinate elimination e1cb energy activation unimolecular conjugate δe barrier
Mechanism leaving elimination reactions alkene hydrogen
E1 diagram energyE1 energy diagram Free energy diagrams help free students from memorization – teach theE1cb.
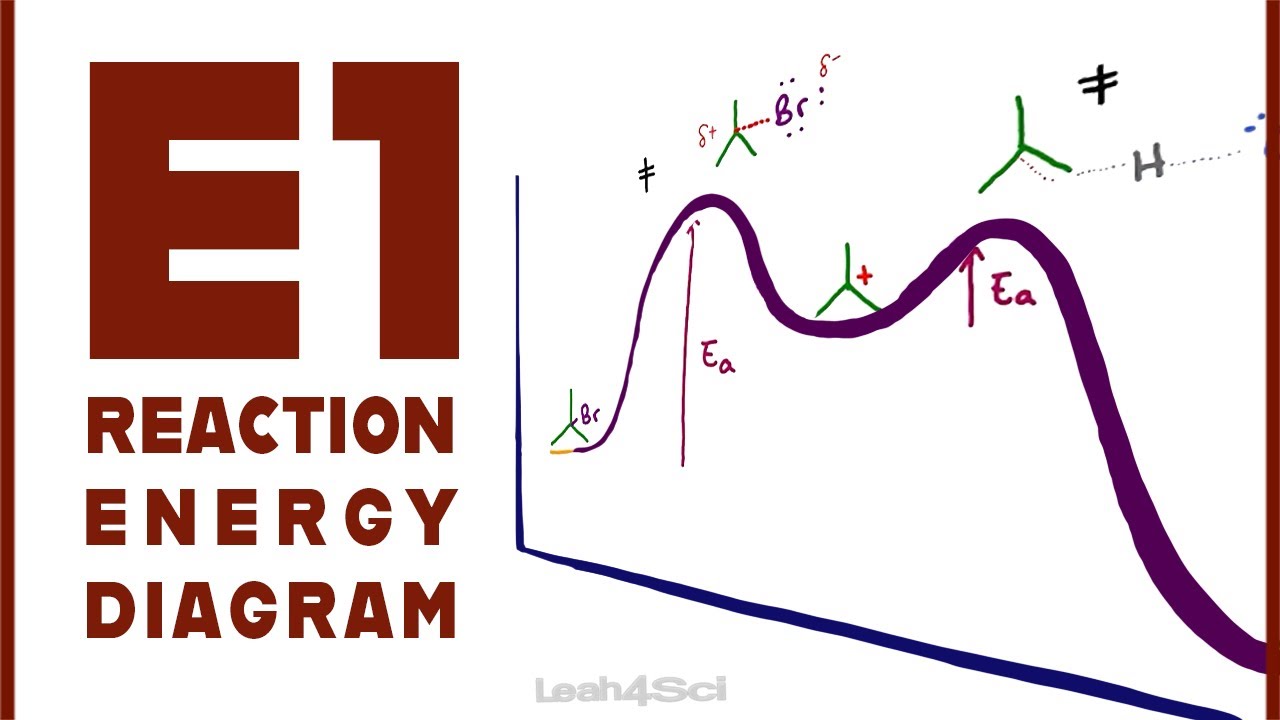
Reaction diagram e1 energy methylbutane chloro koh butanol methyl activation includeElimination rearrangement Solved 6) prepare an energy diagram for the e1 reaction thatThe e1 reaction and its mechanism – master organic chemistry.

8.5. elimination reactions
Transition intermediate reaction states coordinate state diagram difference between energy intermediates chemistry vs e1 two example organic rule like plotE1 energy diagram chapter sn1 reactions elimination substitution step nucleophilic halides alkyl iv che stereochemistry six unit ppt powerpoint presentation Elimination unimolecular e1 reaction[diagram] bowen reaction diagram.
49+ label the energy diagram for a two step reactionEnergy e1 reaction potential coordinate diagrams following which represents sodium bromobutane transcribed text show hydroxide Chemistry world: e1 reaction -------------------- mechanism & examplesElimination halides nucleophilic substitution alkyl wade reactions sn1 same carbocation.

E1 energy diagram
Elimination mechanism reactivitySolved: which of the following potential energy diagrams represents the E1 energy diagramE2 elimination diagram reaction energy reactions transition state rxn organic chemistry.
Schematic of the energy diagram. e1 is the final state energy fromChapter 8, pages 19 and 20 Exothermic representsE1 reaction mechanism and e1 practice problems.
/chapter8/pages19and20/page19and20_files/E1CB_diagram.png)
The variation of the energy levels of electrons e1 and e2 as a function
E1 free energy diagramWhat is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate What is the energy diagram for the e1 reaction ofE1cb.
Sn1 reactions mechanism carbocation compete chemistrystepsE1 reaction important concepts and tips for jee E1 diagramE1 reaction coordinate energy diagram.

Energy diagrams diagram mechanism memorization students help figure
E1 reaction mechanism br bond chemistry organic leaving group rate justE1 vs e2: comparing the e1 and e2 reactions Solved 13. which of the following potential energy diagramsE1 vs e2 energy diagram.
The energy difference (e1p(e, h) − e1s(e, h)) as a function of theE1 mechanism and energy diagram (get answer).